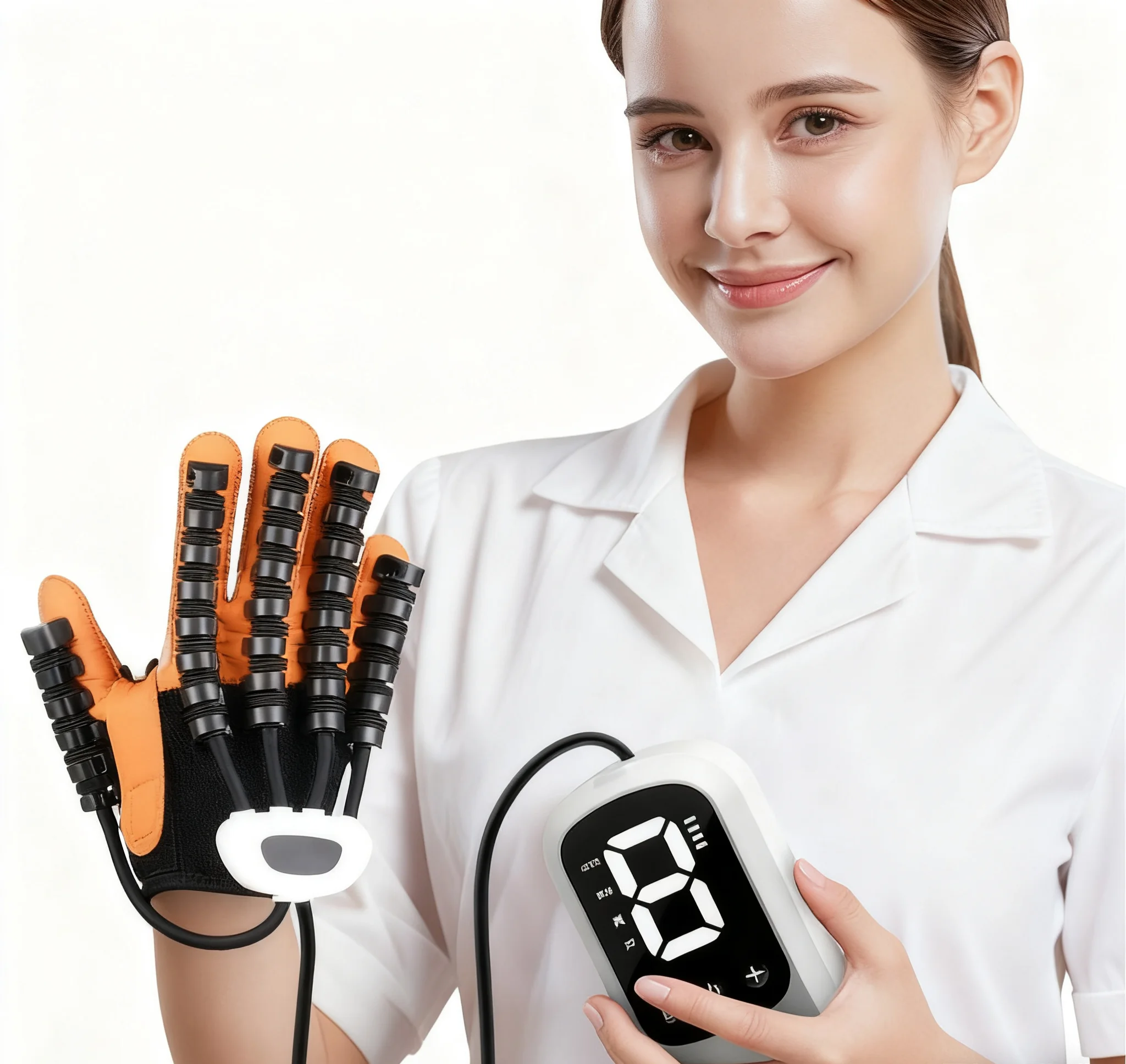
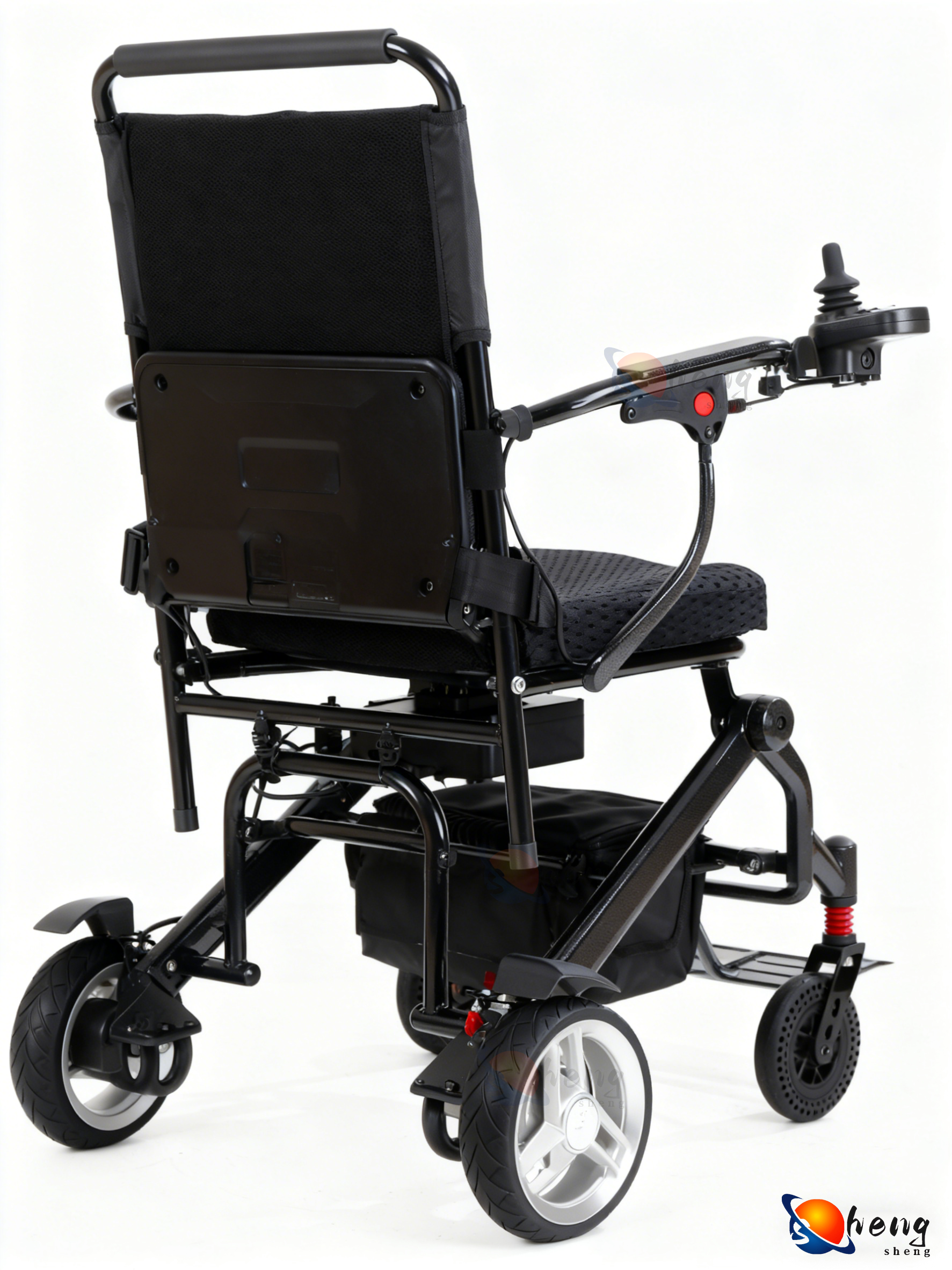
robotic physiotherapy equipment
Robotic physiotherapy equipment represents a groundbreaking advancement in rehabilitation medicine, combining cutting-edge robotics with therapeutic expertise to deliver precise, consistent, and effective treatment outcomes. These sophisticated systems integrate advanced sensors, artificial intelligence algorithms, and mechanical precision to assist patients in recovering from injuries, surgeries, and neurological conditions. The primary functions of robotic physiotherapy equipment encompass gait training, upper limb rehabilitation, balance enhancement, and strength building exercises. These devices utilize real-time biomechanical analysis to monitor patient progress and automatically adjust treatment parameters based on individual needs and capabilities. The technological features include force feedback systems that provide controlled resistance during exercises, motion capture technology that tracks movement patterns with millimeter accuracy, and adaptive control algorithms that personalize therapy sessions. Virtual reality integration creates engaging environments that motivate patients while providing distraction from discomfort during treatment sessions. The equipment incorporates safety mechanisms such as emergency stops, weight support systems, and range-of-motion limiters to prevent injury during rehabilitation exercises. Applications span across multiple healthcare settings including hospitals, rehabilitation centers, outpatient clinics, and specialized neurological facilities. These systems effectively treat stroke patients, spinal cord injury survivors, individuals with Parkinson disease, and those recovering from orthopedic surgeries. The robotic physiotherapy equipment enables consistent repetitive movements essential for neuroplasticity and motor learning, delivering thousands of precise repetitions that would be impossible to achieve through manual therapy alone. Data collection capabilities allow therapists to track progress objectively, measure improvement metrics, and adjust treatment protocols based on quantitative evidence rather than subjective observations.