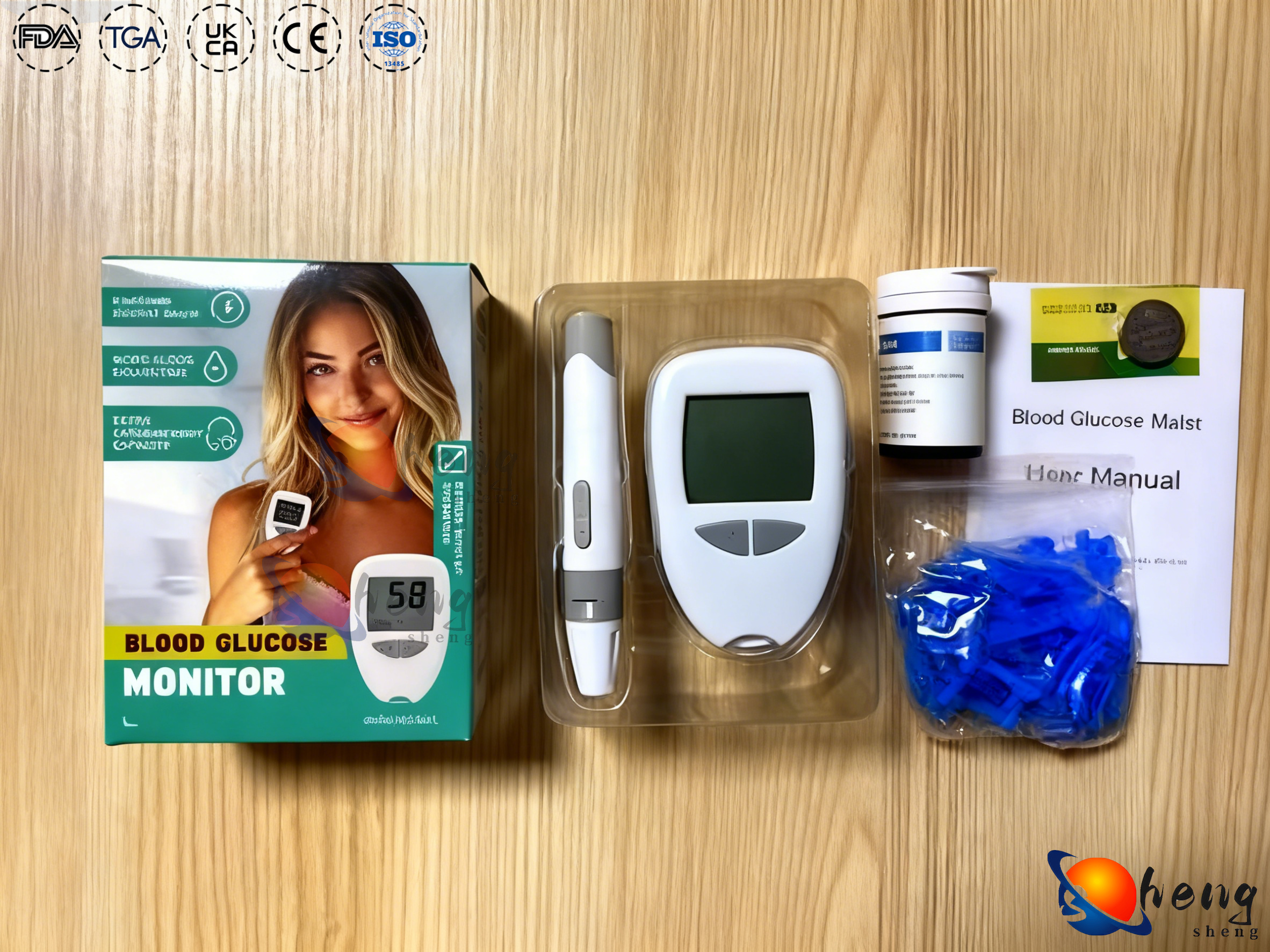
Managing diabetes effectively requires consistent blood sugar monitoring, making the selection of an appropriate glucose monitor a critical healthcare decision. Modern glucose monitors have evolved significantly from their early iterations, incorporating advanced technology to provide accurate readings while maintaining user-friendly interfaces. Understanding the essential features of an effective glucose monitor empowers individuals with diabetes to make informed choices that support their daily health management routines. These medical devices serve as indispensable tools for millions of people worldwide, enabling them to track glucose levels with precision and confidence.
Essential Accuracy Standards for Blood Sugar Testing
Precision Requirements and Clinical Validation
Accuracy represents the most fundamental characteristic of any reliable glucose monitor, as even minor measurement variations can significantly impact diabetes management decisions. Clinical-grade glucose monitors must meet stringent FDA requirements, typically maintaining accuracy within 15% of laboratory reference values for glucose concentrations above 75 mg/dL. This precision standard ensures that users receive dependable readings that healthcare providers can trust when adjusting treatment protocols. Manufacturing quality controls, enzyme stability, and calibration processes all contribute to maintaining consistent accuracy across thousands of test cycles.
Professional healthcare facilities often utilize glucose monitors that undergo rigorous validation testing against laboratory-grade equipment to establish baseline accuracy parameters. The International Organization for Standardization has established specific guidelines that manufacturers must follow to achieve medical device certification for glucose monitoring systems. Regular calibration checks and quality assurance protocols help maintain accuracy throughout the device's operational lifespan, ensuring reliable performance even after extended use periods.
Temperature and Environmental Stability
Environmental factors can significantly affect glucose monitor performance, making temperature stability a crucial feature for consistent accuracy. High-quality glucose monitors incorporate temperature compensation mechanisms that automatically adjust readings based on ambient conditions, preventing false readings caused by extreme temperatures. Storage temperature ranges typically span from -4°F to 104°F, while operational temperatures usually range between 68°F and 104°F for optimal performance. Humidity resistance also plays a vital role in maintaining accuracy, particularly in regions with high moisture levels.
Advanced glucose monitors feature internal sensors that continuously monitor environmental conditions and apply appropriate correction factors to ensure accurate readings regardless of external circumstances. This environmental stability becomes particularly important for individuals who travel frequently or live in regions with significant temperature variations throughout the year. Manufacturers often conduct extensive environmental testing to validate their glucose monitor performance under various conditions, providing users with confidence in their device's reliability.
User Interface Design and Accessibility Features
Display Technology and Readability
Modern glucose monitors incorporate large, high-contrast displays that enhance readability for users with varying vision capabilities, particularly elderly individuals who may experience age-related vision changes. Backlit LCD screens with adjustable brightness settings allow users to obtain clear readings in diverse lighting conditions, from dimly lit bedrooms to bright outdoor environments. Font sizes are typically optimized for easy reading, with bold numerals that stand out clearly against contrasting backgrounds. Some advanced models feature color-coded displays that provide immediate visual feedback about glucose level ranges.
Display orientation and button placement receive careful consideration during glucose monitor design phases to accommodate users with limited dexterity or mobility challenges. Touch-screen interfaces have become increasingly popular, offering intuitive navigation while reducing the number of physical buttons required for operation. Multi-language support expands accessibility for diverse user populations, ensuring that language barriers do not prevent effective diabetes management. Voice-guided instructions and audio alerts further enhance accessibility for visually impaired users.
Ergonomic Design and Portability
Compact dimensions and lightweight construction make modern glucose monitors highly portable, enabling users to maintain consistent monitoring routines regardless of location or activity level. Ergonomic grip surfaces and rounded edges enhance comfort during handling, reducing the likelihood of accidental drops or slippage during testing procedures. Many glucose monitors feature protective carrying cases that safeguard the device while providing organized storage for test strips, lancets, and other essential supplies. Battery life optimization ensures extended operation periods between charging cycles or battery replacements.
Durability testing validates that glucose monitors can withstand daily use conditions, including minor impacts, moisture exposure, and temperature fluctuations commonly encountered in real-world environments. Scratch-resistant screens and impact-resistant housings protect internal components while maintaining aesthetic appearance over extended use periods. Slip-resistant textures and contoured designs accommodate users with arthritis or other conditions affecting manual dexterity, ensuring comfortable operation for individuals with diverse physical capabilities.

Advanced Testing Speed and Sample Requirements
Rapid Result Generation
Contemporary glucose monitors deliver test results within 5-15 seconds, dramatically reducing waiting times compared to older generation devices that required 30 seconds or longer for accurate readings. This rapid response capability encourages more frequent testing by minimizing the time investment required for each glucose check, ultimately supporting better diabetes management through increased monitoring consistency. Advanced biosensor technology and optimized enzymatic reactions enable these shortened testing cycles without compromising measurement accuracy. Fast result generation particularly benefits busy individuals who need to integrate glucose testing into demanding daily schedules.
Microprocessor optimization and efficient data processing algorithms contribute to the impressive speed improvements seen in modern glucose monitors, while maintaining the computational accuracy required for reliable medical measurements. Some premium models feature countdown timers that display the remaining processing time, helping users understand when results will be available. Quick result generation also reduces anxiety associated with glucose testing, as users spend less time waiting for potentially concerning readings. Emergency situations particularly benefit from rapid glucose assessment capabilities.
Minimal Blood Sample Volume
Advanced glucose monitor technology requires extremely small blood samples, typically 0.3 to 1.0 microliters, reducing discomfort and making testing more comfortable for users who need frequent monitoring. Capillary action test strips automatically draw the required blood volume, eliminating guesswork about sample adequacy while preventing waste from insufficient samples. This minimal sample requirement particularly benefits elderly users, children, or individuals with circulation issues who may have difficulty producing larger blood drops. Reduced sample volumes also mean less invasive finger pricking and faster healing of puncture sites.
Precision engineering in test strip design enables reliable glucose measurement from these tiny sample volumes through optimized chemical reactions and sensitive detection systems. Alternative site testing capabilities allow blood collection from less sensitive areas such as forearms or palms, further reducing discomfort associated with frequent glucose monitoring. Advanced wicking technology ensures complete sample uptake even from small blood drops, preventing test failures due to insufficient sample volume. These innovations make glucose monitoring more accessible for individuals who previously found testing too uncomfortable or difficult.
Data Management and Connectivity Options
Memory Storage and Historical Tracking
Comprehensive data storage capabilities allow glucose monitors to maintain detailed testing histories spanning several months, enabling users and healthcare providers to identify patterns and trends in blood sugar levels over extended periods. Most modern devices store 200-500 test results with accompanying timestamps, creating valuable datasets for treatment optimization and lifestyle correlation analysis. Advanced models calculate average glucose levels over different time periods, providing meaningful statistical summaries that support clinical decision-making. Automatic data organization by date and time eliminates manual record-keeping requirements while ensuring accurate historical documentation.
Memory management features typically include automatic deletion of oldest entries when storage capacity is reached, ensuring continuous data collection without user intervention. Some glucose monitors offer expandable memory through removable storage cards or cloud synchronization services that preserve unlimited testing histories. Date and time stamping accuracy depends on internal clock maintenance, with many devices featuring automatic time updates through wireless connectivity. Statistical analysis functions help identify testing frequency patterns and glucose level distributions across different periods.
Wireless Connectivity and Smartphone Integration
Bluetooth connectivity enables seamless data transfer between glucose monitors and smartphones, tablets, or other mobile devices, creating comprehensive digital health records that can be easily shared with healthcare providers. Dedicated mobile applications provide advanced data visualization tools, trend analysis capabilities, and medication tracking features that enhance diabetes management beyond basic glucose monitoring. Cloud-based data storage ensures that testing information remains accessible even if devices are lost, damaged, or replaced. Wireless connectivity also enables automatic software updates that can improve device functionality over time.
Integration with electronic health record systems streamlines clinical consultations by providing healthcare providers with detailed glucose monitoring data before appointments. Push notifications and reminders through connected devices help users maintain consistent testing schedules, improving adherence to monitoring protocols. Some glucose monitors support multiple device connections, allowing family members or caregivers to monitor glucose levels remotely when necessary. Privacy and security protocols protect sensitive health information during wireless transmission and cloud storage operations.
Cost-Effectiveness and Long-Term Value
Test Strip Economics and Ongoing Expenses
The long-term cost of glucose monitoring primarily derives from test strip expenses rather than initial device purchase prices, making strip affordability a crucial factor in glucose monitor selection decisions. Generic test strips often provide significant cost savings compared to brand-name alternatives, though users must verify compatibility and accuracy standards before switching from original manufacturer strips. Insurance coverage varies significantly between different glucose monitor brands and models, with some providers offering preferred pricing for specific manufacturers. Bulk purchasing options and subscription services can reduce per-test costs for frequent users who require multiple daily glucose checks.
Cost-per-test calculations should include not only test strip prices but also lancet costs, alcohol prep pads, and other consumable supplies required for complete glucose monitoring routines. Some glucose monitor manufacturers offer patient assistance programs that provide discounted or free supplies for qualifying individuals with limited financial resources. Pharmacy loyalty programs and manufacturer rebates can further reduce ongoing glucose monitoring expenses for budget-conscious users. Comparing total cost of ownership over one-year periods provides more accurate economic assessments than focusing solely on initial equipment costs.
Durability and Warranty Coverage
Quality construction and robust engineering contribute to glucose monitor longevity, with most reputable devices offering 2-5 year operational lifespans under normal use conditions. Comprehensive warranty coverage typically includes manufacturer defects, calibration issues, and component failures, providing users with protection against unexpected replacement costs. Extended warranty options may be available for additional fees, offering peace of mind for users who depend heavily on their glucose monitoring equipment. Water resistance ratings and drop-test certifications indicate device durability under challenging real-world conditions.
Manufacturer support services include technical assistance, replacement part availability, and repair services that extend device useful life beyond initial warranty periods. Some companies offer trade-in programs that provide credits toward newer glucose monitor models when upgrading from older devices. Regular firmware updates can extend device functionality and improve performance over time, adding value to the initial investment. Customer service quality and responsiveness become important factors when technical issues arise with glucose monitoring equipment.
Safety Features and Clinical Integration
Alert Systems and Emergency Notifications
Advanced glucose monitors incorporate multiple alert mechanisms that notify users when glucose levels fall outside predetermined safe ranges, providing crucial early warnings that can prevent dangerous hypoglycemic or hyperglycemic episodes. Audible alarms, visual indicators, and vibration alerts ensure that warnings are noticed even in noisy environments or when visual attention is focused elsewhere. Customizable alert thresholds allow users to set personalized notification levels based on their individual glucose management goals and medical provider recommendations. Some models feature escalating alert intensities that become more prominent if initial warnings are not acknowledged promptly.
Smart notification systems can distinguish between different types of glucose level concerns, providing specific guidance for hypoglycemia versus hyperglycemia situations through color-coded displays or differentiated alert sounds. Emergency contact notification features enable automatic text messages or phone calls to designated family members or healthcare providers when critical glucose levels are detected. Integration with medical alert systems ensures that emergency responders have access to current glucose information during medical emergencies. Sleep mode modifications adjust alert sensitivity during nighttime hours while maintaining safety monitoring capabilities.
Clinical Data Sharing and Healthcare Provider Integration
Seamless clinical integration capabilities enable healthcare providers to access glucose monitoring data remotely, facilitating more effective diabetes management through continuous oversight rather than relying solely on periodic office visits. Standardized data export formats ensure compatibility with various electronic health record systems used by different medical facilities and provider networks. Automated reporting features can generate comprehensive glucose monitoring summaries that highlight trends, patterns, and potential concerns for clinical review. Real-time data sharing enables healthcare providers to make immediate treatment adjustments when concerning glucose patterns are identified.
Patient portal integration allows users to share glucose monitor data directly with their medical teams through secure online platforms, streamlining communication and reducing administrative burdens for both patients and providers. Clinical decision support tools can analyze glucose monitoring data alongside other health metrics to provide comprehensive diabetes management recommendations. Telemedicine compatibility enables remote consultations where healthcare providers can review current glucose monitor readings in real-time during virtual appointments. Privacy compliance with healthcare regulations ensures that glucose monitoring data sharing meets strict confidentiality requirements.
FAQ
How often should I calibrate my glucose monitor for accurate readings
Most modern glucose monitors do not require regular user calibration, as they come pre-calibrated from the manufacturer and maintain accuracy throughout their operational lifespan. However, you should verify accuracy periodically by comparing your glucose monitor readings with laboratory results during routine medical appointments. If you notice consistent discrepancies or if your device has been exposed to extreme temperatures or physical impact, contact the manufacturer for guidance on potential calibration issues or device replacement needs.
What factors can cause inaccurate glucose monitor readings
Several factors can affect glucose monitor accuracy, including expired test strips, contaminated blood samples, insufficient blood volume, extreme temperatures, high altitude, dehydration, and certain medications that interfere with glucose measurement chemistry. Proper hand washing before testing, using fresh test strips, ensuring adequate blood sample size, and storing your glucose monitor within recommended temperature ranges help maintain measurement accuracy. Always follow manufacturer instructions precisely and consult your healthcare provider if you suspect accuracy problems.
Can I use generic test strips with my brand-name glucose monitor
Generic test strips may be compatible with certain glucose monitor models, but you should verify compatibility and accuracy before switching from manufacturer-recommended strips. Some generic strips meet the same quality standards as brand-name alternatives and can provide significant cost savings, while others may compromise accuracy or reliability. Consult your healthcare provider and check with your insurance company about coverage options for both generic and brand-name test strips before making changes to your glucose monitoring supplies.
How do I choose between basic and advanced glucose monitor features
Your glucose monitor feature requirements depend on your specific diabetes management needs, technology comfort level, and budget considerations. Basic models with essential accuracy and simple operation may be sufficient for occasional users, while advanced features like smartphone connectivity, data analysis, and alert systems benefit individuals requiring frequent monitoring or complex treatment regimens. Consider discussing your lifestyle, monitoring frequency, and technology preferences with your healthcare provider to determine which glucose monitor features will best support your diabetes management goals.